Top 10 Most Influential Inventions from Egypt
When we think of Egypt, pyramids, mummies, pharaohs, and sphinxes are some of the things that come up to our mind. Egypt consists of a rich history tracing all the way back to over 10,000 BCE - its Dynastic Period starting at 3,150 BCE with the rise of Ancient Egyptian civilization. What made Egyptian civilization so successful is that it came from the familiarization of the Nile River and its predictable conditions, thus giving an abundance of crops due to its annual flooding and rich fertile soil. The Old Kingdom (or also known as the Age of the Pyramids) also marked a significant milestone to both architecture, cultural, and technology advances that changed the rest of Egyptian history. Along with Mesopotamia, it's no doubt that Egypt contributed a vast collection of technology and inventions - some of that we use today. From hieroglyphics to mathematics, this list presents the top 10 most influential inventions from Egypt.
Also known as Ancient Egyptian writing. Along with the Mesopotamians, the Egyptians also invented writing in the medium of pictograms and symbols, which were used to convey information about an event, person, or object; however, this was of limited use. Later on, the Egyptians developed different ways to communicate - including logograms and other elements used to describe abstract things. Then there were hieroglyphics, which were a combination of logograms, phonograms, ideograms, and other symbols. It was believed that egyptian writing was dedicated to the Egyptian god Thoth, who was the inventor of languages and writing. It was a strong medium of communication that not only the Egyptians were effective in conveying information through stories, literature, knowledge, and documentation, but allowed us to understand how Egyptian society worked.
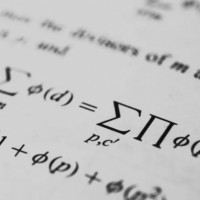
While the Mesopotamians developed their fair share of mathematics, Egyptians also developed their own number system which revolved in arithmetic, mostly for calculating fractions and multiplication tracing back to approximately 3000 BC. Although they weren't as abstract as the Greeks, they were the first people to invent solving quadratic equations. The ancient Egyptians also knew some of the math that's daily used in the modern world - including algebra, geometry and calculating the surface area and volume of objects. Egyptian mathematics was also based on the number ten, which had its own symbols for tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands, etc. Additionally, Egyptian multiplication - with the emphasis of the power of two, is surprisingly linked to the same binary system that's used in modern computers - with the value either being doubled or its first number being placed back into it. Without their clever usage of mathematics, the Egyptians wouldn't have pyramids.

The Egyptians were one of the earliest people to invent clocks - in the form of obelisks, and one of the earliest people to split whole days into hours. It's reported that obelisks were built as early as 3500 BCE. The moving shadows around the obelisk were used to determine the time in day, hence why it was effective as a shadow clock. Not only that obelisks played a role in telling time, but it also played a major role in religion, particularly in the buildings of temples and honoring the gods. Later on, starting in 1500 BCE, the Egyptians invented a specialized shadow clock, which not only more accurately indicated the day time, but divided the time of night into fifty parts, with the addition to twilight hours both morning and evening.

The Egyptians were the first people to use papyrus as a medium for writing, with the material first being produced from papyrus plants approximately 4000 BCE. The durability of papyrus stood out exceptionally from other writing materials due to Egypt's rather dry climate; it was in other words, the "paper" of Egyptians. The process of making papyrus was believed that the stem of the plant was cut into stripped first, then placed side to side in a hard material, and was soaked in order to rot. Finally, it is believed that they may have been glued together. The layers were then beaten into a piece of paper and was put up for drying, where it would be polished with the use of stone or other hard materials.

You can also credit the Egyptians for being majorly responsible for maintaining dental hygiene. The creation of toothpaste traces back to 5000 BCE, which was composed with rock salts, pumice, burnt eggshells, and ox hooves. This was effective for hygiene as Egyptians had struggle with cleaning their teeth, and often had cavities and abscesses inside their teeth. Not only they are credited for making toothpaste, but they also were the first people to invent the toothbrush, which consisted of twigs with worn off ends.

Surprisingly, most of our comfort household objects traces back to Ancient Egypt. Prehistoric evidence shows that people carved furniture over 30,000 years ago in the Neolithic times, but it was the egyptians who are taken credit for their innovative creations of furniture. Chairs were first invented by the Egyptians around 3100 BC during the Archaic Period of Egypt, which were upholstered with leather or cloth. The chairs that were invented in Egypt weren't as the same as modern chairs we use today; the seats were much lower back then. Tables were later made approximately in 2500 BCE which were composed of alabaster and wood. The Egyptians also invented beds, and were the first people to create chests.

Ink was not only of great importance along with papyrus in Egypt, but it opened the gates to writing and art. Yet surprisingly, both the Egyptians and the Chinese are credited for the invention of Ink. Tracing back to 2,600 BCE, ink was used by the Egyptians for writing on papyrus. The making of ink is composed of a combination of organic and inorganic materials, including ocher, iron, and lead, which were also accompanied by phosphate, chloride, sulfide, and carboxylate ions.

It's no doubt that Egyptian culture had an emphasis for cosmetics. The appearance of Egyptians not only had a strong connection to holiness and spirituality, but it determined their social class as well - the more cosmetics a person wore, then the more likely he or she was regarded to be wealthy. The usage for makeup was traced all the way back to 4000 BCE. Egyptian makeup not only was applied to women, but also for men. Eye make up was made of black kohl and grepond eye paint, while green cosmetics were made of malachite. Black eye make up was composed of galena ore. It was also believed that kohl and mesdemet pigments provided protection from sickness, bugs, and the sun.

Based on the evidence of some paintings of the Egyptian tombs, the Egyptians were also one of the first people to invent door locks. The creation of door locks is traced back to 4000 BCE, which was a pin tumbler lock composed of wood. A pin tumbler lock had a pole fastened to the door, which was accompanied by a bolt consisting of pins that slid towards the pole. The locks that Egyptians used was a lot larger than most of the locks we use today.

We all rely on calendars to remember our schedules and traditions, and that's all thanks to the Ancient Egyptians. The Egyptian calendar consisted of three seasons (those which are attributed to their agricultural lifestyle), 12 months with 30 days for each month, which totaled up to 360 days. Later on, they included five extra days in order to align with the solar year. These five extra days were spent for religious holidays and traditions, mostly for the honor of Osiris, Iris, Horus, Seth, and Nephthys.