Top 10 Worst Computer Viruses
The birth of the Morris Worm in 1988 sparked a new era of concern for computer security, marking the beginning of what would become a complex battleground between cybercriminals and cybersecurity professionals.Computer viruses have evolved significantly over the years, moving far beyond simple pranks and moving into the realm of serious criminal activity and even international cyber warfare. From stealing personal and financial data to locking users out of their own files for a ransom, these digital bugs have become a major global concern.
What actually makes a virus successful, or should we say, effective? Well, there are a couple of factors. Stealth is key - the best viruses are often those that can infiltrate a system without detection, silently working in the background. They might exploit known vulnerabilities in software, or use social engineering tricks to get users to unintentionally download and execute them. Then, once they've set up shop in a system, they propagate. They spread as widely and quickly as possible, infecting other systems through networks, email attachments, or even USB drives.
But the worst viruses? They're not just stealthy and prolific, they're destructive too. They cause serious damage, whether that's wiping out critical system files, stealing sensitive data, or even recruiting the infected system into a botnet for use in larger scale cyber attacks.
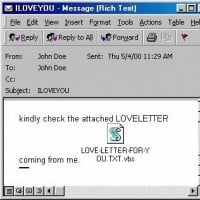 The ILOVEYOU virus, also known as "Love Bug," emerged in 2000 from the Philippines. This infamous worm was propagated through email, enticing recipients to open a "LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU" attachment, leading to system compromise and rapid replication to all contacts in the recipient's address book.
The ILOVEYOU virus, also known as "Love Bug," emerged in 2000 from the Philippines. This infamous worm was propagated through email, enticing recipients to open a "LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU" attachment, leading to system compromise and rapid replication to all contacts in the recipient's address book. This virus has infected over 10 million computers since 2000. And what happened you may ask. You get a file named "LOVELETTER". You're computer gets infected. Pretty bad. It doesn't exist anymore. But people have reported it's still out there. If you get a file titled "LOVELETTER". Do not open it. Or you're infected
Thank GOD its not here. But legend has it that people have reported its still out there
If it were still here, this would be a nightmare!
 Debuting in 2004, the Sasser worm exploited a vulnerability in non-updated Windows XP and 2000 systems. The virus could infect a system without user interaction, causing issues with system stability and network traffic due to its rapid replication capabilities.
Debuting in 2004, the Sasser worm exploited a vulnerability in non-updated Windows XP and 2000 systems. The virus could infect a system without user interaction, causing issues with system stability and network traffic due to its rapid replication capabilities.
 As one of the first widely known ransomware attacks, CryptoLocker emerged in 2013, encrypting victims' files and demanding a Bitcoin payment for their release. It was typically spread through infected email attachments and compromised websites.
As one of the first widely known ransomware attacks, CryptoLocker emerged in 2013, encrypting victims' files and demanding a Bitcoin payment for their release. It was typically spread through infected email attachments and compromised websites. Imagine someone barfing all over your xbox, then asking for $500 so they can clean it up LIGHTLY, and then does it again the next day.
That's CryptoLocker for you.
Ransomware in general is the worst - it honestly makes me vie for the days of fake antivirus programs.
Worst virus ever. It encrypts your computer's data, and demands a ransom of a high price to get it back. And even if you manage to delete the virus from Safe Mode or something, your files WILL STILL BE ENCRYPTED.
 Identified in 1998, the CIH Virus, also known as Chernobyl, is a destructive virus that can overwrite critical information on the system's BIOS chip, rendering the system unbootable. It is also capable of overwriting data on the user's hard drive.
Identified in 1998, the CIH Virus, also known as Chernobyl, is a destructive virus that can overwrite critical information on the system's BIOS chip, rendering the system unbootable. It is also capable of overwriting data on the user's hard drive. An old virus that could destroy Windows and the first few sectors (Master Boot Record or Master File Table). Some certain variants can even destroy the BIOS and/or CMOS by overwriting it with random bytes of data - essentially making the computer a paperweight. Patched in BIOSes newer than 2001/2002, this virus is ancient by today's standards. The virus first emerged in 1998 and caused around $1 Billion US in damages, thought to infect over 60 Million machines worldwide. No one needs to worry about this virus these days, considering the fact that it only infects Windows 9x OSes (95, 98/98SE, ME), and is patched in any motherboard manufactured past 2002.
This virus spreaded so quickly that it had 10% of computer shut down at the time! It also took about 6 days to be removed from a computer. The way it worked was that it would replicate itself infinitly and move to other computers.
This virus just the worst. After you watch something disgusting, listen to music on websites, or play violent games. You get a pop up saying your personal computer has been blocked, and they show screenshots and make you wonder "Wow. My actions can be watched and taken to the police." And it asks you to pay a fine of 200$ (Correct me if I'm wrong) and after it popped up. When you try to log into your computer. You get the virus page instead of the info. If you get this page, don't listen to it. It's just made by a homeless guy who tries to get money from you.
Kills your computer, forever displaying a Nyan Cat...
 This sophisticated worm, discovered in 2010, specifically targeted supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems used in industrial applications. It's most well-known for disrupting Iran's nuclear enrichment program by causing centrifuges to spin out of control.
This sophisticated worm, discovered in 2010, specifically targeted supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems used in industrial applications. It's most well-known for disrupting Iran's nuclear enrichment program by causing centrifuges to spin out of control.
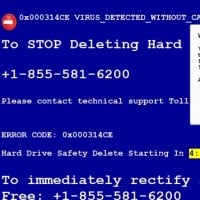 Identified in 2007, Zeus, also known as Zbot, is a Trojan horse primarily used to steal banking information by man-in-the-browser keystroke logging and form grabbing. It is often spread through phishing schemes or drive-by downloads.
Identified in 2007, Zeus, also known as Zbot, is a Trojan horse primarily used to steal banking information by man-in-the-browser keystroke logging and form grabbing. It is often spread through phishing schemes or drive-by downloads.'The most complex malware ever found.' Why is it not higher?
Shuts down your computer and ASKS you if you want to delete all your stuff
Mydoom is most dangerous worm in all computer viruses. Mydoom was first sighted on January 26, 2004.
I wonder why this isn't higher on the list...
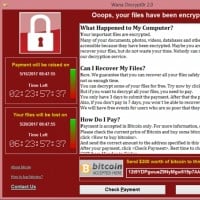 This ransomware attack, occurring in May 2017, spread through a vulnerability in Windows' Server Message Block protocol. WannaCry encrypted users' files, demanding Bitcoin payments for their release, and affected numerous institutions worldwide, including the NHS in the UK.
This ransomware attack, occurring in May 2017, spread through a vulnerability in Windows' Server Message Block protocol. WannaCry encrypted users' files, demanding Bitcoin payments for their release, and affected numerous institutions worldwide, including the NHS in the UK. Cerber, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) that first emerged in 2016, is notable for its evasion techniques and voice-recorded ransom messages. It uses sophisticated encryption to lock users' files and demands a ransom to decrypt them.
Cerber, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) that first emerged in 2016, is notable for its evasion techniques and voice-recorded ransom messages. It uses sophisticated encryption to lock users' files and demands a ransom to decrypt them.Look it up. Not popular, but if you got it on your computer, you would be screwed.